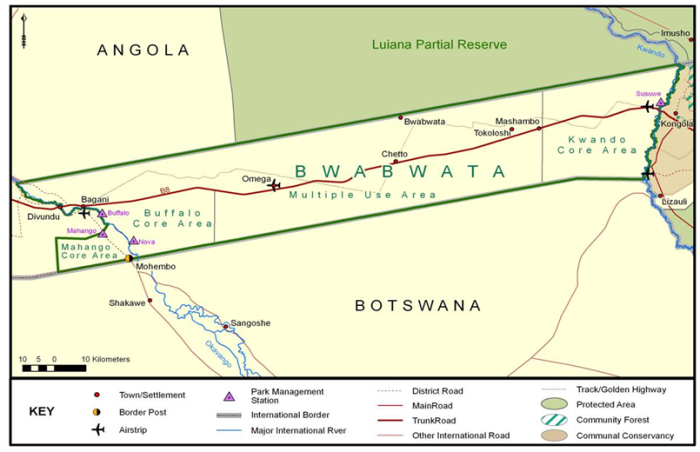
The Trust lies north and south of the Trans-Caprivi Highway between the Kwando River and Okavango Rivers in West Caprivi and encompasses a total area of about 625,000 ha. It is bordered on the south by Botswana and on the north by Angola. A large part of the area has been designated as a protected area named Bwabwata National Park. The Tourism Core Area along the banks of the Okavango River and a settlement area north of the Trans-Caprivi Highway have been de-gazetted and are managed as communal areas.
Ministry of Environment And Tourism Namibia
Bwabwata is named after a village in the reserve and means “the sound of bubbling water”. In 1999, after a government decision, the Caprivi Game Park and the Mahango Game Reserve were merged and later the Kwando River triangle were added to become Bwabwata National Park.
The Park is divided into three core areas (Buffalo, Kwando and Mahango) to control conservation and tourism and to one multiple use area, where the resident communty can live and practice subsistance farming.
The Flora and Fauna of the park is rich and diverse, thanks to not only the abundant natural resources but also the long-term sustainable management of them by the residents of the park. Common trees include the Zambezi teak, wild seringa, manketti, false mopane and camelthorn tree. Several rare large mammal and bird species are found in Bwabwata National Park. Elephants are regular visitors while moving across the borders, but other species like the African buffalo, hippopotamus, roan antelope, sable antelope and Burchell’s zebra are also common. Lions, leopards, cheetah and spotted hyena can also be found within the park. There are more than 300 different bird spieces in the park, which makes Bwabwata an internationally important bird area even supporting globally threatened species.